The procedure for calculating the minimum number of traverse points in Stack
The procedure for calculating the minimum number of traverse points is as follows:
A) Measure the stack diameter to within 0.3175 cm (1/8 inch)
1) Insert a long rod or pitot tub e into the duct until it touches the opposite wall.
2) Mark the point on the rod where it meets the outside of the port nipple.
3) Remove the rod, measure, and record this length to the far wall, Lfw
4) With a tape measure (or rod if stack is hot), measure the distance from the outside of the port nipple to the near wall and record this length to the near wall, Lnw.
5) Calculate the diameter of the duct from this port as D = Lfw -Lnw
B) Repeat for the other port(s) and then average the D values.
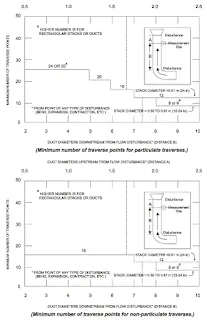
C) Measure the distance from the sample port cross-sectional plane to the nearest downstream disturbance (designated Distance A).
D) Measure the distance from the sample port cross-sectional plane to the nearest upstream disturbance (designated Distance B).
E) Calculate the number of duct diameters to the disturbances by dividing Distance A by D, and Distance B by D.
F) Use Picture in Method 1 for particulate traverses (or Figure 12 for velocity traverses), determine where Distance A diameters meets the graph, then where Distance B diameters meets the graph, and select the higher of the two minimum numbers of traverse points.





0 Comments